Overview
Similarly to Coreform Cubit, Coreform Flex has been carefully designed to support maximum flexibility for automation by Python. The following modes of automation are supported:
- Use of Python within Coreform Flex GUI application.
- Use of Python within journal files executed via Coreform Flex’s “batch” mode.
- Use of Coreform Flex’s Python module (
flex.py) into an external Python session.
We’ll discuss each of these below
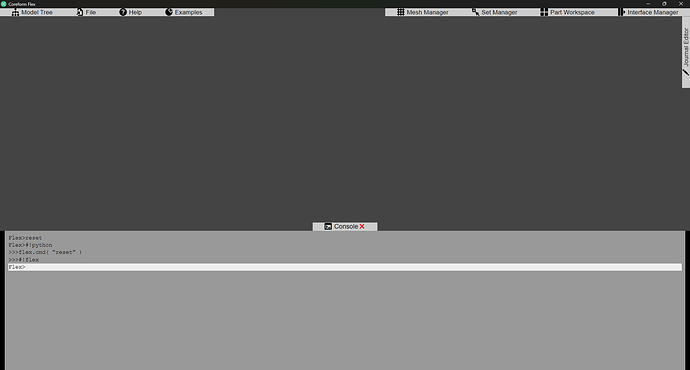
Python within Coreform Flex GUI application
Using the Console within the application you can issue Flex commands or use Flex Python to issue commands. For example:
Flex>reset # This is a Flex Command
Flex>#!python # This is a shebang that switches to Python interpreter mode
>>>flex.cmd( "reset" ) # This uses the Coreform Flex Python API to issue the 'reset' Flex Command
>>>#!flex # This is a shebang that switches to Flex interpreter mode
To replicate these commands, specifically the shebangs, don’t use the comments (# Comment) with the shebangs. For example, recommend doing:
reset
#!python
flex.cmd( "reset" )
#!flex
Python within a command-line Coreform Flex
Coreform Flex can be executed as a command-line tool, however it currently operates in a slightly different manner than Coreform Cubit. In short, Coreform Flex currently supports a “batch” mode of operation of the coreform_flex executable with a Coreform Journal File (.cjf). This mode permits the user to provide a .cjf file that contains Flex commands, but supports shebang-ing to switch to Python mode.
# Windows Powershell command example
PS > & 'path\to\coreform_flex.exe' --headless --batch my_journal.cjf
# Contents of 'my_journal.cjf'
reset
open "my_cf_file.cf"
#! python
import numpy
t = numpy.linspace( 0, 1, 7 )
time_str = " ".join( [ str( val ) for val in t ] )
flex.cmd( f"intervals my_interval additional_time_values [ {time_str} ]" )
Note that Coreform Flex ships with its own Python executable & environment. However, unlike Coreform Cubit, it does not yet support installing additional modules.
Use of Coreform Flex’s Python module
The Coreform Flex Python module is located at bin/coreform/flex.py within your installation directory. For example: C:\Program Files\Coreform Flex 2024.8\bin\coreform\flex.py on Windows. Thus, from another Python environment (minimum version: python 3.8) you can do the following:
import sys
path_to_flex = r"C:\Program Files\Coreform Flex 2024.8\bin\coreform"
sys.path.append( path_to_flex )
import flex
To import the flex module into the session. Then you can submit Flex commands as strings to the flex.cmd() module. Note that the Flex Command Language only supports "string" notation (strings only support double-quotes), thus it’s best-practice to pass strings with single-quotes to flex.cmd():
import sys
import numpy, scipy, sympy, matplotlib
path_to_flex = r"C:\Program Files\Coreform Flex 2024.8\bin\coreform"
sys.path.append( path_to_flex )
import flex
flex.cmd( 'reset' )
flex.cmd( 'open "my_cf_file.cf"' )
t = numpy.linspace( 0, 1, 7 )
time_str = " ".join( [ str( val ) for val in t ] )
flex.cmd( f"intervals my_interval additional_time_values [ {time_str} ]" )
# etc.
matplotlib.pyplot.plot( t, result_values )