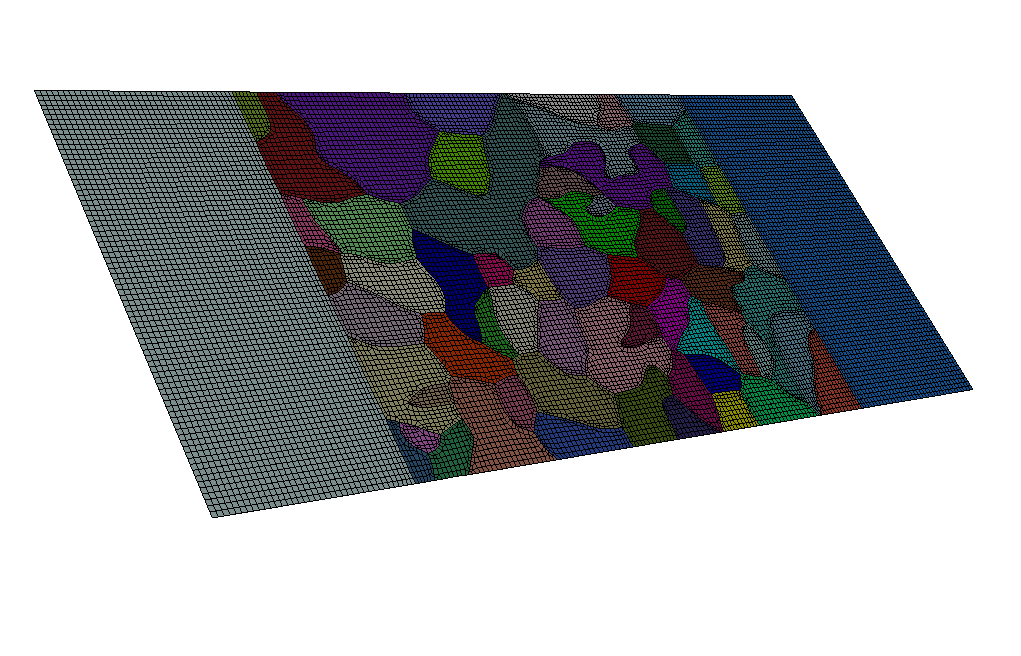
Hi Team,
I’m trying to create a 2D model of a microstructure from the attached .spn file (please change the extension from .txt to .spn) using Sculpt, but I’m running into difficulties. I initially tried setting “nelz = 0,” but that caused Sculpt to end with an error. I also attempted setting “nelz = 1” and “zscale = 0,” but that didn’t result in a successful model generation either.
Below is my Sculpt script, but it still produces a 2.5D model with some thickness, which I want to avoid. I’m looking for a way to generate a true 2D model with no thickness. Any advice or guidance would be greatly appreciated!
Many thanks,
Ondrej
voxels1.txt (59.3 KB)
BEGIN SCULPT
# Dimensions
nelx = 185
nely = 79
nelz = 1
# Scales
xscale = 1.981982e+01
yscale = 1.974684e+01
zscale = 1
# Fixed mesh improvement
smooth = 3
defeature = 1
pillow_curves = true
pillow_boundaries = true
micro_shave = true
#mesh_void = 1
# Variable mesh improvement
opt_threshold = 0.7
pillow_curve_layers = 3
pillow_curve_thresh = 0.3
# Solver
laplacian_iters = 5
max_opt_iters = 50
# Output
input_spn = voxels1.spn
exodus_file = mesh.e
END SCULPT
Hi Ondrej,
Sculpt produces 3D models. It does not create 2D meshes. You could just create a 2D grid and assign the material numbers.
Does this work? Note that it does take a couple of minutes to assign all the quad faces individually.
#!cubit
reset
create surface rectangle width 1
#
# For some reason python reads this file all as one line. I anticipated
# being able to get the number of rows and columns. I'm guessing here from
# the factorization of the number of entries. 79 * 185 = 14615
curve 1 interval 79
curve 2 interval 185
mesh surface 1
print("Starting . . .")
#!python
with open(r"C:\Users\kgmer\Downloads\voxels1.txt", "r") as fp:
line = fp.readlines()
materials = line[0].split()
print(len(materials), materials[0])
for i, m in enumerate(materials):
result = cubit.cmd(f'block {m} add face {i+1}')
#!cubit
draw block all
Karl
The other idea would be to create the 2.5-dimensional model in sculpt and then just export the surface mesh. If we assume that you create a unit cube centered at the origin, the front face will be at z = 0.5. You should be able to something like the code below to just extract the 2D elements out of the existing mesh.
I will warn you that this is the idea, but I didn’t run your model or test the script below.
Karl
#!python
# add a tolerance on the z coordinate
front_surfaces = cubit.parse_cubit_list('surface', 'with z_coord > 0.49')
for surf in front_surfaces:
# I don't know how sculpt names the blocks/underlying volumes
# but, you could be more sophisticated than this for assigning block ids
block_id = cubit.get_next_block_id()
cubit.cmd(f'block {block_id} add surface {surf}')
# assuming you want a 2D element set the type to QUAD
cubit.cmd('block {block_id} element type QUAD')
#! cubit
export mesh 'mesh.e' overwrite
Thank you so much, Karl, for taking the time to look into this. Let’s give your suggestions a try — I’m sure we can make one of them work.
Thank you again for the suggestion, Karl. The following works:
mesh_2d.e (824.8 KB)
mesh_3d.e (1.0 MB)
z_target = 0
tolerance = 1e-6
existing_volumes = cubit.parse_cubit_list(‘volume’, ‘all’)
existing_blocks = cubit.parse_cubit_list(‘block’, ‘all’)
existing_volumes_str = " ".join(map(str, existing_volumes))
existing_blocks_str = " ".join(map(str, existing_blocks))
front_surfaces = cubit.parse_cubit_list(‘surface’, f’with z_coord > {z_target - tolerance} and z_coord < {z_target + tolerance}’)
if len(front_surfaces) == 0:
print(“No surfaces found near z = 0”)
else:
# Step 1: Create a list of tuples (volume_id, surface_id) by finding the volume for each surface
surface_volume_map = []
for surf in front_surfaces:
# Loop through each volume to find which volume the surface belongs to
for vol_id in existing_volumes:
volume_surfaces = cubit.parse_cubit_list('surface', f'in volume {vol_id}')
if surf in volume_surfaces:
surface_volume_map.append((vol_id, surf))
break
# Step 2: Sort the list of surfaces by the volume ID
sorted_surfaces = [surf for vol_id, surf in sorted(surface_volume_map)]
# Step 3: Initialize block_id to start from 1000
block_id = 1000
# Step 4: Iterate over the sorted surfaces and create 2D blocks
for surf in sorted_surfaces:
cubit.cmd(f'block {block_id} add surface {surf}')
cubit.cmd(f'block {block_id} element type QUAD') # Set the element type to 2D QUAD
# Increment block_id for the next surface
block_id += 1
# Step 5: Delete 3D volumes but exclude those that contain the surfaces we are working with
front_surfaces_str = " ".join(map(str, sorted_surfaces))
cubit.cmd(f'delete volume all except with surface {front_surfaces_str}')
# Step 6: Delete old blocks but keep the newly created 2D blocks
if existing_blocks_str:
cubit.cmd(f'delete block {existing_blocks_str}')
# Step 7: Export the mesh with the existing 2D surfaces
cubit.cmd("export mesh 'mesh_2d.e' overwrite")